Polygon Layer 2 Solution
Polygon, formerly known as Matic Network, is a Layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum that provides faster and cheaper transactions, while maintaining high levels of security and decentralization. Its interoperability with Ethereum makes it an attractive option for developers looking to build dApps on a scalable and secure platform.
The list of projects built on the Polygon network includes a variety of projects from business and fintech solutions to metaverses and GameFi. In total, as it was established in autumn 2022, there are more than 53 thousand decentralized applications (dApps) on Polygon.
The doubts that accompanied some on the eve of the transition of Ethereum from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, that Layer-2 scaling solutions would go into the shadows, turned out to be unjustified. The Ethereum Merge has become one of the steps on the way to improving the network but has not saved users from such nuances as gas fees and transaction speed. Thus, Polygon is still gaining popularity as in the space of Web3 it is gaining distribution in traditional industries.
By the way, we talked about the Merge in detail in one of our previous articles: Ethereum Merge Explained
About what a Polygon is in 2023, we want to explore.
Blockchain Features and Services of Polygon
Polygon blockchain is known for its high scalability, low transaction fees, and fast processing times. It is built on top of the Ethereum network and uses a modified version of the Plasma framework.
Here are some of the key features and advantages of Polygon:
- Faster and Cheaper Transactions: Polygon achieves faster and cheaper transactions by using a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This allows for faster transaction processing times and lower fees.
Polygon has a high throughput capacity, which allows for faster processing of transactions at lower costs. The average gas fees on Polygon vary depending on the level of network congestion and the complexity of the transaction, but they are generally much lower than on Ethereum, with some transactions costing only a few cents in gas fees.
You can see the gas fees tracker for the Polygon network.
- Interoperability: Polygon is interoperable with Ethereum, which means that developers can easily port their Ethereum-based applications to Polygon without much hassle. This makes it easier for developers to build decentralized applications on Polygon.
The purpose of developing an interoperable network like Polygon is to enable seamless communication and data transfer between different blockchains and their respective ecosystems. This allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in building dApps, as developers can leverage the strengths of different blockchains and integrate them into a single application. Additionally, interoperability can help to reduce transaction costs and improve overall scalability, as transactions can be processed across multiple blockchains simultaneously.
- Scalability: Polygon is designed to be highly scalable, which means that it can handle a large number of transactions without slowing down or becoming congested. This is achieved through its Layer-2 solution, which allows it to process transactions off-chain and then settle them on the Ethereum mainnet.
Layer-2 projects like Polygon provide scalability by taking some of the burden off of the Layer-1 blockchain. They accomplish this by conducting transactions off-chain, and then only submitting a result to the Layer-1 blockchain. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be processed by the Layer-1 blockchain, which can help to reduce congestion and increase transaction throughput.
- Security: Polygon is highly secure, thanks to its PoS consensus mechanism, which ensures that only those who hold a certain number of tokens can participate in the network. This makes it difficult for malicious actors to attack the network.
Polygon has undergone multiple security audits by reputable third-party firms such as Quantstamp and Trail of Bits, which helps to identify and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities.
Quantstamp is a blockchain security company that provides auditing and security solutions for smart contracts and decentralized applications. In the case of Polygon, Quantstamp can provide security by auditing the smart contracts and dApps built on the Polygon network to identify and fix any potential vulnerabilities or security issues. This can help ensure that the applications built on Polygon are secure and reliable for users. Additionally, Quantstamp can provide ongoing security monitoring and support for the Polygon network to ensure that it remains secure and protected against potential threats.
Trail of Bits is a cybersecurity firm that provides auditing services for blockchain projects, including Polygon. The company conducts regular security audits to ensure that the platform is secure and free from vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
The audit process typically involves a thorough review of the platform's code, architecture, and security protocols. The auditors will identify any potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for addressing them. The process also includes testing the platform's resilience to various types of attacks and verifying that all transactions are properly secured.
Spearbit is another firm that routinely tests the Polygon zkEVM. The result is set out in a report on the official website of Polygon.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) with Polygon
Polygon offers a wide range of projects and services for developers to build and deploy decentralized applications on its network.
One of the most significant developments is the introduction of zkEVM, a layer 2 scaling solution that uses zero-knowledge proofs to increase the speed and efficiency of smart contract execution. This technology allows developers to create complex dApps that can run on the Polygon network without the high gas fees associated with Ethereum.
Another development is the launch of Polygon Miden, a decentralized exchange (DEX) that offers users a fast and secure way to trade cryptocurrencies. Miden is built on the Polygon network and offers a range of features including liquidity pools, limit orders, and automated market-making.
Polygon has also introduced Supernets, which are specialized networks that allow developers to build custom solutions for specific use cases. These networks are designed to offer high performance and low latency, making them ideal for applications such as gaming, NFTs, and DeFi.
Finally, Polygon ID is a unique identity solution that allows users to securely manage their identity across multiple blockchain networks. This technology provides a single sign-on experience for users, allowing them to access dApps and other services without having to repeatedly enter their credentials.
The purpose of these developments is to make the Polygon network more efficient, scalable, and versatile. By introducing these new technologies, Polygon is positioning itself as a leading blockchain platform that can meet the needs of a wide range of industries and use cases. As the demand for blockchain-based solutions continues to grow, Polygon is well-positioned to become a key player in the space.
Recent developments and achievements of Polygon
Polygon developments are frequently adopted by blockchain and cryptocurrency product and service developers. The network, which debuted in 2017, has established strong relationships with the Web3 industry.
What is the purpose of expanding the Polygon and blockchain projects, explains Polygon’s co-founder, Sandeep Nailwal: “If there are large-scale usage of these apps and people see that there is actual value being created with Web3 applications, the regulators will come along and they will see that this is a legitimate industry.”
Here is an example of several projects that Polygon is closely associated with:
Chainlink. Polygon has integrated with Chainlink, a decentralized oracle network that provides secure and reliable external data to smart contracts. This helps to prevent manipulation and ensures the accuracy of data used in the network.
Aave. Polygon has collaborated with Aave, a leading DeFi protocol, to bring its lending and borrowing services to the Polygon network, providing users with faster and cheaper transactions.
Kyber network. The Kyber Network and Polygon protocols' mutually beneficial impact aims to enhance the liquidity and accessibility of decentralized finance (DeFi) on the Polygon network.
By adopting blockchain and crypto, traditional industries can stay at the forefront of technological innovation and attract new customers who are interested in these emerging technologies.
Here are some examples of the collaborations between Polygon and non-blockchain global brands:
Starbucks. In 2022, it was reported that Starbucks was exploring the use of blockchain technology, including the Polygon network, to improve the traceability and transparency of its supply chain.
Adobe. Behance, Adobe's social network, now supports the Polygon cryptocurrency platform to enable users to showcase their non-fungible tokens (NFTs) based on Polygon more easily. This integration is aimed at promoting an eco-friendlier approach for artists to create NFTs, which Behance started supporting in 2020.
Disney. By partnering with Polygon, Disney can leverage its expertise to develop and implement new blockchain-based solutions that can help enhance the company's operations and provide new opportunities for growth.
Environmental Impact and Social responsibility
Polygon's sustainability goals stated a path for becoming "carbon-negative" in 2022 and "climate positive" thereafter. Polygon has already attained Network Carbon Neutrality.
Carbon offsetting is the process of reducing greenhouse gas emissions in one area to compensate for emissions produced in another area. Carbon offset projects can involve activities such as reforestation, renewable energy development, or capturing methane gas from landfills. By offsetting its carbon emissions, Polygon aims to mitigate its impact on the environment and contribute to the global effort to combat climate change.
Polygon's Green Manifesto is a commitment to building a sustainable and environmentally friendly blockchain ecosystem. The manifesto outlines several goals, including reducing the network's carbon footprint, promoting energy efficiency, and supporting green initiatives. The aim of the manifesto is to encourage the adoption of sustainable practices by the blockchain industry as a whole and to create an eco-friendlier future for decentralized technologies. By prioritizing sustainability, Polygon hopes to demonstrate that blockchain technology can be both innovative and responsible, and that it has a role to play in tackling the global climate crisis.
Polygon is currently working on a number of projects expanding the environmental agenda. Sustainable programs are collaborating with climate action leaders, technologists, and scientists to come up with regenerative solutions. On the Polygon website, you can find detailed cases in documents like this one.
Polygon, in addition to supporting and advocating for environmental projects and organizations, seeks to alleviate economic injustice through Web3.
Polygon Labs teamed with Mercy Corps Ventures in March 2023 to develop initiatives to assist underbanked populations as well as plans to adopt blockchain solutions for underprivileged and low-income individuals and communities in emerging economies.
The partnership is expected to result in the establishment of blockchain pilots that will be available to more than a billion people worldwide who are lacking in debit cards or bank accounts.
Other areas of work are based on research and outreach; Polygon and Mercy Corps are planning a series of blockchain hackathons with developers and launching a “blockchain bootcamp roadshow in markets where Mercy Corps has a presence, aimed to provide educational and informational sessions for local educational institutions, NGOs, and other organizations looking to improve operations through blockchain technology.”
According to one of Polygon's blog posts:
“Before Ethereum’s move to proof of stake, minting an NFT on Ethereum produced roughly 150kg of C02, the equivalent of watching 4,320 hours of Netflix; minting on Polygon resulted in just .4g of C02, the equivalent of watching Netflix for only 40 seconds.”
Polygon is collaborating with Virtua, the NFT ecosystem, and the metaverse platform to promote sustainability in the blockchain industry, and is now developing an infrastructure for green NFTs, which are NFTs produced and distributed using environmentally friendly practices. This involves the use of renewable energy and a decrease in carbon emissions.
So, Polygon network is taking steps towards promoting sustainability and reducing its impact on the environment. By committing to carbon neutrality, using energy-efficient algorithms, developing green NFTs, partnering with sustainable projects, and promoting education and awareness, Polygon is leading the way towards a more sustainable blockchain future.
Transaction Speed, Interoperability, and Centralization: Comparison with Other Blockchains
Ethereum is the most well-known and widely used blockchain for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. It is a Layer-1 solution, meaning that it is the primary blockchain layer where transactions are processed and recorded. However, Ethereum has faced scalability issues, leading to high gas fees and slow transaction times.
Polygon, as we said before, is a Layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum that aims to address these issues. It offers faster and cheaper transactions by processing them off-chain and then settling them on the Ethereum mainnet. Polygon also supports interoperability between different blockchains, making it a popular choice for developers looking to build cross-chain dApps.
Biannca Smart Chain (BSC) is another blockchain that has gained popularity due to its lower fees and faster transaction times compared to Ethereum. It is also a Layer-1 solution but uses a different consensus mechanism called Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA), which allows for faster block times and lower gas fees. BSC is often criticized for its centralization, as it is controlled by the centralized exchange Binance.
Solana is a relatively new blockchain that has gained attention for its high-speed transactions and low fees. It is also a Layer-1 solution but uses a unique consensus mechanism called Proof of History (PoH), which allows for faster processing times and higher throughput. Solana is often seen as a potential competitor to Ethereum due to its scalability and developer-friendly features.
Overall, the main difference between these networks lies in their approach to scalability and transaction processing. Developers must weigh the trade-offs between security, decentralization, speed, and cost when choosing which network to build their dApps on.
Let’s see the statistics:
MATIC Price Analysis
MATIC token is a cryptocurrency that was launched in April 2019. It is the native token of the Polygon network, a Layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum. The aim of Polygon is to improve the scalability and usability of the Ethereum network by providing faster and cheaper transactions.
In terms of technical analysis, the MATIC token has had a volatile price history. In its early days, it had a relatively low trading volume and price, but as the Polygon network gained more attention and adoption, the token's price began to rise rapidly.
One of the most notable price movements for MATIC occurred in May 2021 when the cryptocurrency market experienced a significant sell-off. During this time, MATIC saw a sharp decline in price, dropping from around $2.50 to under $0.75 in just a few days. However, since then, MATIC has been able to recover and has seen some significant price increases.
The price of a crypto token can be affected by various factors such as supply and demand, market sentiment, adoption and acceptance, regulatory changes, network upgrades and developments, and overall market conditions.
Additionally, the development of new features or partnerships can also have a positive impact on the price of a crypto token as it increases adoption and usage.
By analyzing the historical behavior of a crypto token, technical analysis can provide insights into potential buying and selling opportunities, as well as help traders manage risk by setting stop-loss orders or profit targets.
Polygon (MATIC) now has a circulating supply of 9 194 469 069 MATIC tokens, with a total maximum supply of 10 000 000 000 MATIC tokens. Let's take a look at the graph of the MATIC price change over time.
The price of MATIC has been unpredictable during the last six months, but since the end of January 2023, the token has begun to gain growth more consistently and has now settled at the average price of the past three months. The token's price has risen by 41.15% in six months.
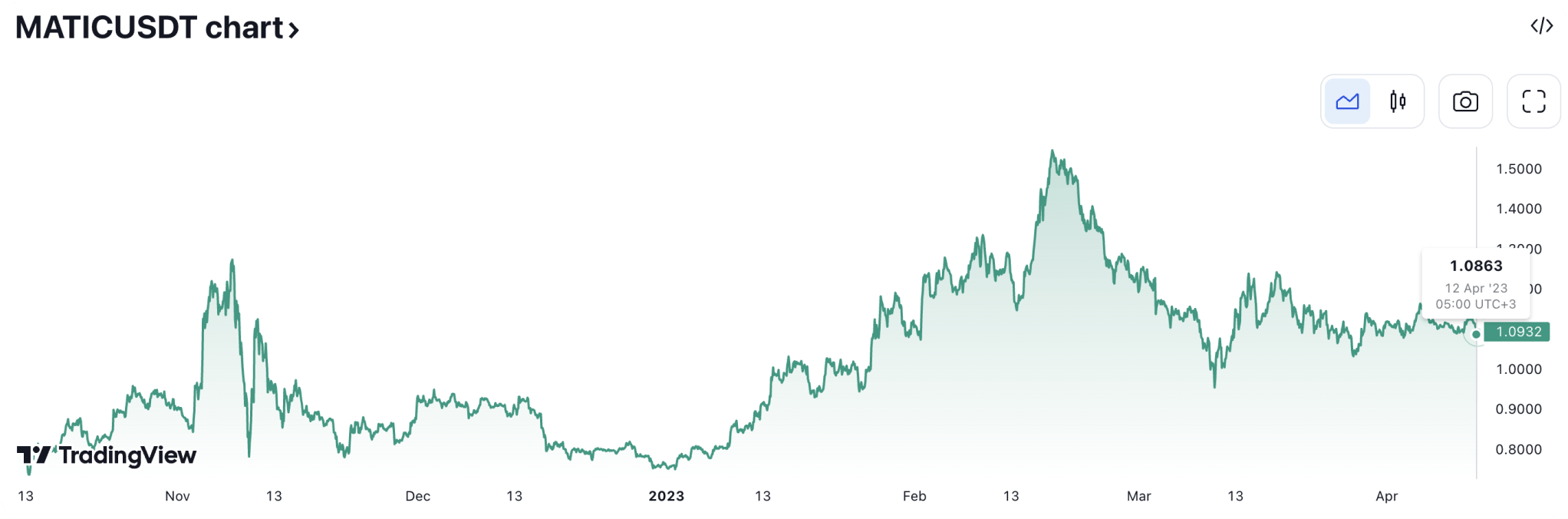
The monthly value gain demonstrates the signs of price stabilization:
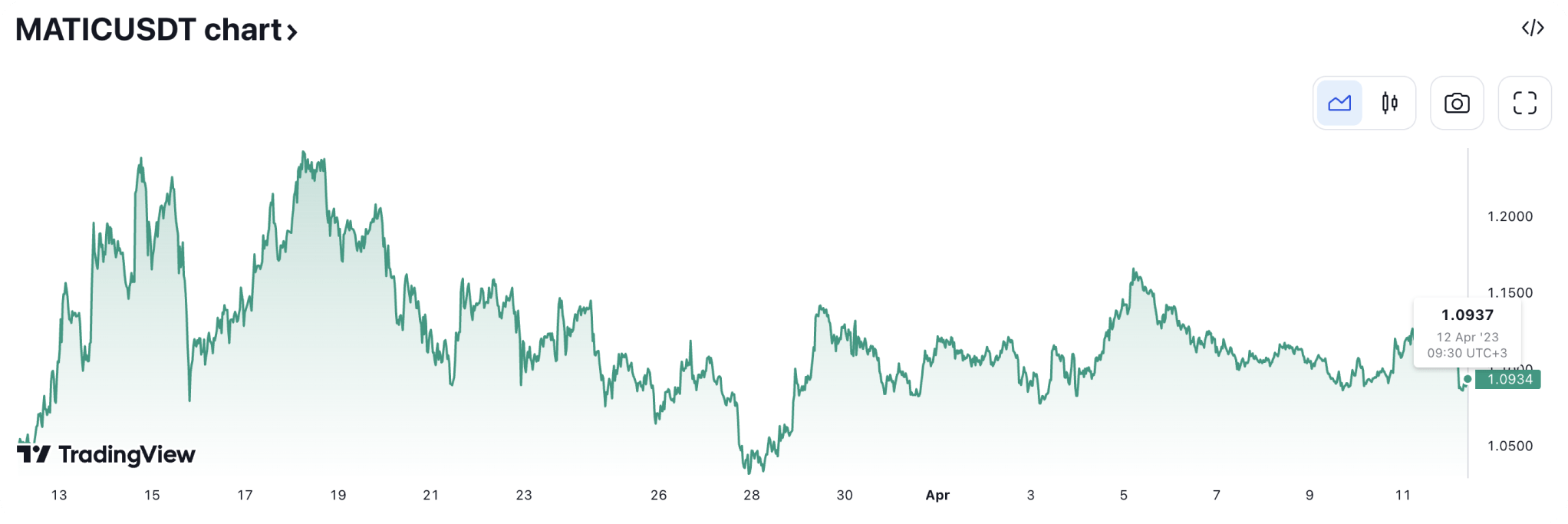
What is the MATIC movement today:
To understand candlestick basics to make accurate predictions in more detail, check out our article on crypto candlestick charts.
MACD and Stochastic Oscillator are two of the most used indicators among traders. There are tips on how to put these into action in the hyperlinks.
Polygon Ecosystem Pro et Contra
To provide the fullest view of Polygon, it also becomes important to describe the downsides that network users come across. Even though Layer-2 solutions were established to reduce network congestion, it may still be a challenge for Polygon network.
The risk of congestion on the Polygon network arises when there is a high volume of transactions being processed at the same time, which can lead to slower transaction times and higher transaction fees. This can occur when there is a surge in user activity on the network or during periods of high market volatility.
Polygon recently faced a blockchain quark in February 2023 that affected 157 blocks, creating delays in transaction finality. Sandeep Nailwal, co-founder of Polygon, identified the problem as a network bug, which was quickly fixed. A chain reorganization, or a “reorg”, caused blocks to stop producing for several minutes.
“Reorgs occur when network nodes get out of sync with each other, and two unique chains of blocks are produced concurrently,” according to the Protos notice. This could be the result of a bug, network slowness, or malicious action. When nodes sync again, one canonical version of the chain is retained, and the invalid'fork' blocks are ignored.”'
Another aspect to keep in mind when it comes to a decentralized blockchain network is the number of validators that confirm that the network is not prone to the monopoly of a few individuals
On blockchain networks, a varied number of validators operate. As an example, the most extensive Ethereum network has a few hundred thousand validators. The parallel with the Binance Smart Chain network, which is available for bitoftrade swaps, is striking. Only 21 validators provide BSC security.
It is vital to remember that the number of network validators is greatly affected by the type of consensus mechanism chosen by developers, as well as the staking amount that a user must stake to get the status of a validator.
There are currently 100 active validators on the Polygon network. More information can be found in the Polygon Wiki.
Users and experts are slightly skeptical about Polygon's level of decentralization due to the small number of participants involved in network administration. Such fears sometimes extend to networks with decentralized structures. For example, as stated, the top ten UniSwap delegates control 42.35% of the votes.
In August 2022, Cyber Capital founder, Justin Bons, began a Twitter discussion in which he noted that Polygon “is still incredibly unsecure & centralized.” According to Bons, compromising the network requires five keys, four of which are possessed by the network's creators. He advocated that the designers give Polygon DAO or MATIC token holders ownership of the smart contract admin key.
In January 2023, concerns were raised about the unbiased nature of the Polygon hard fork management, with only 15 validator teams participating in the voting process, according to the statement.
When we consider both the advantages and negative outcomes, we can see a broader context. By assessing risks, we strengthen our strategy for analyzing specific projects. The fullness of information is especially important in high-risk industries like blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Polygon is one of the most sophisticated initiatives in decentralized finance, and it is spreading its influence on the everyday world by including traditional sectors in the crypto and blockchain adoption process.
The Polygon network is now available for swaps with the lowest gas fees at https://bitoftrade.com/trading/
Check out the bitoftrade YouTube channel to learn how to start trading on Polygon:
How to Add Polygon network to MetaMask
How to Add Polygon tokens to MetaMask
How to Swap on Polygon network via bitoftrade
Very soon, Polygon will be ready to test out with the newest bitoftrade product — AllPay Widget, a a customizable web object that can be embedded into any webpage, enabling your users to link their wallets, make cryptocurrency payments, trade fungible tokens, and purchase NFT all without ever leaving the hosting website. See more.
Follow our social media to stay up to date with the latest all-in-one bitoftrade platform news: